Feature Models (FMs) are one of the most used artefacts to describe the set of products in an SPL in
terms of features and relationship among them. In FMs, features are hierarchically arranged in a tree like structure. In addition, cross–tree constraints can be used to connect features. Figure 1 shows an
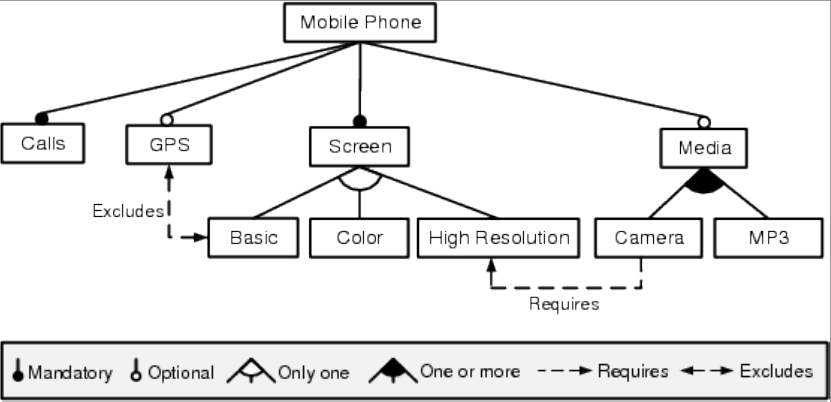
example of an FM describing a mobile phones SPL, using the most common notation and its represented products. There are different proposals for FM notations but most of the proposals have the following common elements:
- Mandatory: a child feature has a mandatory relationship with its parent feature when it appears in a
product whenever its parent does. In Figure 1, Screen has a mandatory relationship with Mobile Phone ,
i.e. any mobile phone must have a screen.
- Optional: a child feature has an optional relationship with its parent feature when the child can
appear or not in a product whenever its parent does. In the example in Figure 1, Media has an
optional relationship with Mobile Phone , i.e. A mobile phone can have support for media features or
not depending on the configuration chosen.
- Or–relationship (also known as OneOrMore): a set of child features has an or–relationship with its
parent when one or more child features can be selected when the parent is. Figure 1 contains an
or–relationship between Camera and MP3 with Media . Whenever Media is present in a product, Camera ,
MP3 , or both have to be present.
- Alternative (also known as OnlyOne): a set of child features have an alternative relationship with
their parent when one and only one of them can be selected in a given product whenever their parent
is selected. Figure 1 shows an alternative relationships among Basic , Colour and High Resolution and Screen ,
so a given mobile phone can only have a specific type of Screen in a product.
- Requires, Excludes: Cross–tree relationships like A requires B means that whenever feature A appears in
a product, feature B must also appear. Also, a relationship like A excludes B means that both features cannot appear in the
same product at the same time. Figure 1 shows two examples of these kinds of relationship: the Camera requires a High Resolution screen and the GPS excludes the Basic screen.
Automated analysis of feature models
The AAFM deals with extracting information from FMs by using computer–aided mechanisms. SPL
engineers use the information to improve their business strategies as well as to take technical decisions.
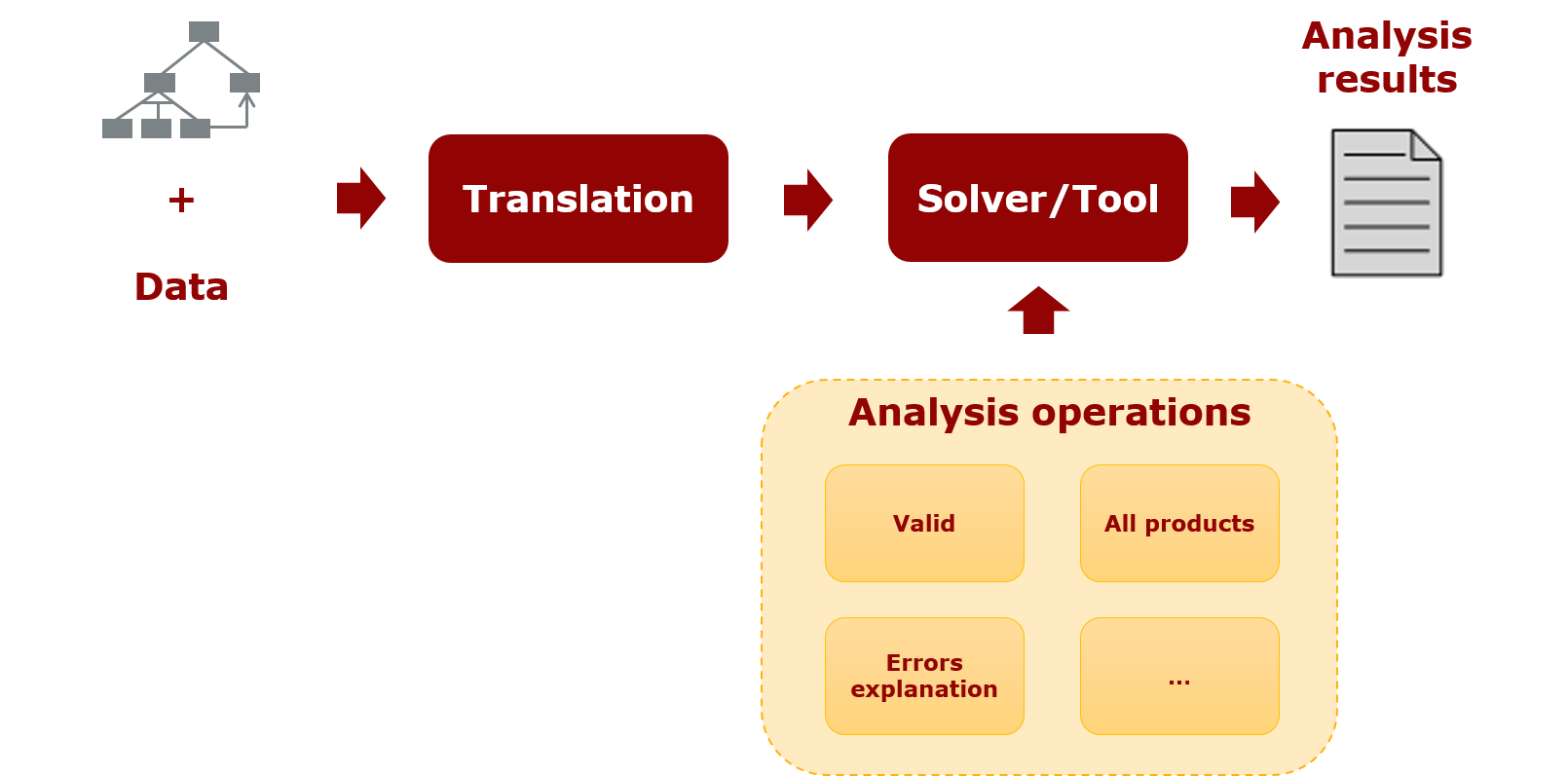
The process to extract such information is shown in the figure below. It starts by translating the features
and relationships encoded in the FM and any other additional information (e.g. market share ) to
a knowledge base described in logic paradigm. Later, queries to the knowledge base can be performed
using existing solvers or tools thus, obtaining the analysis results. In the paper reported by
Benavides et al., different analysis operations on
FMs were reported. According to that study, we present the most referenced ones:
- Finding out if a product is valid. This operation checks if a product (i.e. set of features) belongs to
the set of products represented by an FM or not. It is helpful for SPL engineers and managers to
determine whether a given product is available in an SPL.
- Obtaining all products. This operation lists the products represented by an FM. It allows practitioners
to identify the final products that they can manage in their SPL.
- Calculating the number of products. This operation counts the number of products of an FM. This
provides information about the size and complexity of the SPL represented by an FM. It is commonly
used to perform more complex operations such as calculating the amount of reuse metrics of an SPL.
For example, in the example of Figure 1a there are fourteen products.
- Detecting errors. The large number of different features used in an FM increases its complexity as
well as the probability of introducing errors. There are several types of errors that can be detected by
using the AAFM. For example, it is important to determine if an FM is void, i.e. whether it represents
no product at all because of contradicting relationships. Another common error is the detection of
dead features, i.e. features that cannot appear in any of the products derived from the model. Dead
features are clearly undesired since they are the result of a wrong domain modelling.
- Explaining errors. As shown before, there are circumstances where FMs contain errors. In such situations, it is important to assist on resolving them. An explanation operation takes an FM as input
and a set of previously identified errors, trying to provide insights to correct them.
These operations are performed automatically using different approaches. Most of them translate FMs
into specific logic paradigms such as propositional logic, constraint programming or description logic.
Others propose ad–hoc algorithms and solutions to perform these analyses. Finally, these analysis capabilities can also be found in several commercial and open source tools such as pure::variants 1 ,
SPLOT, FaMa or FAMILIAR.